linux上的access()函数判断文件是否存在、打印时间
日期:2014-05-16 浏览次数:21092 次
linux下的access()函数判断文件是否存在、打印时间
一、access函数
功能描述:
检查调用进程是否可以对指定的文件执行某种操作。
?
用法:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int access(const char *pathname, int mode); ?
?
参数:
pathname: 需要测试的文件路径名。 ?
mode: 需要测试的操作模式,可能值是一个或多个R_OK(可读?), W_OK(可写?), X_OK(可执行?) 或 F_OK(文件存在?)组合体。
?
返回说明:
成功执行时,返回0。失败返回-1,errno被设为以下的某个值
EINVAL: 模式值无效 ?
EACCES: 文件或路径名中包含的目录不可访问
ELOOP : 解释路径名过程中存在太多的符号连接
ENAMETOOLONG:路径名太长
ENOENT:? 路径名中的目录不存在或是无效的符号连接
ENOTDIR: 路径名中当作目录的组件并非目录
EROFS: 文件系统只读
EFAULT: 路径名指向可访问的空间外
EIO:? 输入输出错误
ENOMEM: 不能获取足够的内核内存
ETXTBSY:对程序写入出错
?
例如:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
if((access("test.c",F_OK))!=-1)
{
printf("文件 test.c 存在.\n");
}
else
{
printf("test.c 不存在!\n");
}
if(access("test.c",R_OK)!=-1)
{
printf("test.c 有可读权限\n");
}
else
{
printf("test.c 不可读.\n");
}
if(access("test.c",W_OK)!=-1)
{
printf("test.c 有可写权限\n");
}
else
{
printf("test.c 不可写.\n");
}
if(access("test.c",X_OK)!=-1)
{
printf("test.c 有可执行权限\n");
}
else
{
printf("test.c 不可执行.\n");
}
return 0;
}
?运行结果如下:
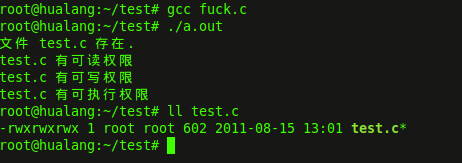
二、如果在C中打印当前时间
下面是一个打印系统当前时间的小例子,函数的语法暂时就不列出了,只是会用这些就差不多了
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
time_t now = time(NULL);
char buf[25];
strftime(buf,24,"%Y%m%d",localtime(&now));
printf("%s\n",buf);
strftime(buf,24,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",localtime(&now));
printf("%s\n",buf);
strftime(buf,24,"%y%m%d %H:%M:%S",localtime(&now));
printf("%s\n",buf);
strftime(buf,24,"%y%m%d",localtime(&now));
printf("%s\n",buf);
strftime(buf,24,"%H:%M:%S",localtime(&now));
printf("%s\n",buf);
return 0;
}
?运行结果:
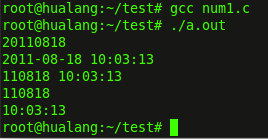
免责声明: 本文仅代表作者个人观点,与爱易网无关。其原创性以及文中陈述文字和内容未经本站证实,对本文以及其中全部或者部分内容、文字的真实性、完整性、及时性本站不作任何保证或承诺,请读者仅作参考,并请自行核实相关内容。
